More than 100,000 evacuated as cyclone threatens India and Pakistan
14 Jun 2023 09:52pm
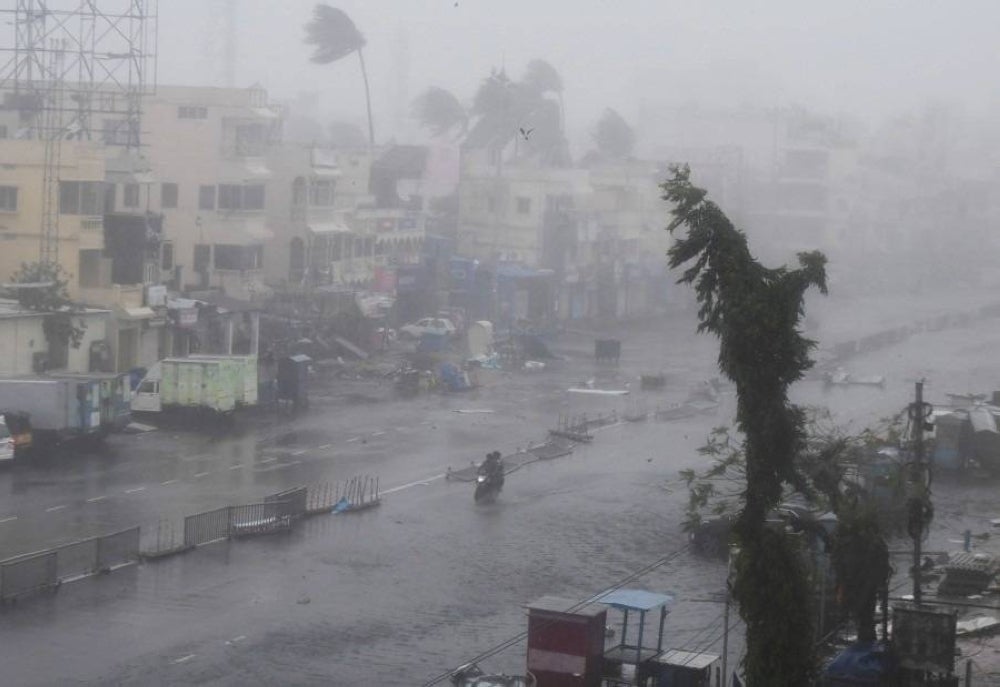

Powerful winds, storm surges and lashing rains were forecast to hammer a 325-kilometre (200-mile) stretch of coast between Mandvi in India's Gujarat state and Karachi in Pakistan. - AFP PIX
Biparjoy, meaning "disaster" in Bengali, is making its way across the Arabian Sea and is expected to make landfall as a "very severe cyclonic storm" on Thursday evening, government weather monitors said.
Powerful winds, storm surges and lashing rains were forecast to hammer a 325-kilometre (200-mile) stretch of coast between Mandvi in India's Gujarat state and Karachi in Pakistan.
India's Meteorological Department predicted the storm will hit near the Indian port of Jakhau late Thursday, warning of "total destruction" of traditional mud and straw thatched homes.
At the usually bustling Jakhau port, sounds of activity were replaced by the howls of wind and the roar of rough seas. Gusts battered more than 30 large fishing boats dragged up out of the water onto the shore, as dozens of stray dogs roamed around the port's entrance.
At sea, winds were already gusting at speeds up to 180 kilometres per hour (112 miles per hour), forecasters said. Wind speeds are predicted to reach 125-135 kph, with gusts up to 150 kph, by the time it makes landfall.
"Over 47,000 people have been evacuated from coastal and low-lying areas to shelter," said C.C. Patel, an official in charge of relief operations in Gujarat.
More were expected to be moved inland throughout Wednesday. India's meteorologists warned of the potential for "widespread damage", including the destruction of crops, "bending or uprooting of power and communication poles" and disruption of railways and roads.
- 'High to phenomenal' -
Pakistan's climate change minister Sherry Rehman said Wednesday that 62,000 people had been evacuated from the country's southeastern coastline, with 75 relief camps set up at schools and colleges.
She said fishermen had been warned to stay off the water and small aircraft were grounded, while urban flooding was possible in the megacity of Karachi, home to around 20 million people.
"We are following a policy of caution rather than wait and see," she told reporters in Islamabad.
"Our first priority is saving lives." The Pakistan Meteorological Department forecast gusts up to 140 kph in the southeastern province of Sindh, accompanied by a storm surge reaching 3.5 metres (11.5 feet).
Fishing has also been suspended along the Gujarat coast, with conditions expected to escalate from "rough to very rough" on Wednesday to "high to phenomenal".
India's armed forces were "ready to provide every possible assistance", Defence Minister Rajnath Singh wrote on Twitter, with disaster response teams mobilised and warning of the risk of "flooding in some low-lying areas".
Five people have been killed in India, including two children who were crushed when a wall collapsed, and a woman was hit by a falling tree while riding a motorbike.
Cyclones -- the equivalent of hurricanes in the North Atlantic or typhoons in the Northwest Pacific -- are a regular and deadly menace on the coast of the northern Indian Ocean, where tens of millions of people live.
Scientists have warned that storms are becoming more powerful as the world gets warmer with climate change. Roxy Mathew Koll, a climate scientist at the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, said cyclones derive their energy from warm waters, and that surface temperatures in the Arabian Sea were 1.2 to 1.4 degrees Celsius warmer than four decades ago.
"Rapid warming in the Arabian Sea, associated with global warming, tends to enhance the heat flux from the ocean to the atmosphere and favour more intense cyclones," Koll told AFP. -Glenda KWEK/AFP
Download Sinar Daily application.Click Here!